https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/crewai-vs-autogen-choosing-the-right-ai-agent-framework
Thursday, 30 January 2025
CrewAI vs. AutoGen: Choosing the Right AI Agent Framework
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/crewai-vs-autogen-choosing-the-right-ai-agent-framework
Wednesday, 29 January 2025
Alibaba's Qwen 2.5-Max: The AI Marathoner Outpacing DeepSeek and Catching OpenAI's Shadow

Alibaba's Qwen 2.5-Max represents a bold leap in the global AI race, combining cutting-edge architecture, multimodal capabilities, and strategic benchmarking to challenge both domestic rival DeepSeek and international leaders like OpenAI.
Origins and Strategic Timing
Developed by Alibaba Cloud, Qwen 2.5-Max builds on the Qwen family of models first introduced in 2023. Its release on January 29, 2025—coinciding with China’s Lunar New Year—signals urgency to counter DeepSeek’s meteoric rise. Just days earlier, DeepSeek’s R1 model had disrupted markets by offering high performance at lower costs, triggering a $1 trillion tech stock selloff. Alibaba’s rapid response highlights China’s intensifying AI competition, with ByteDance and Tencent also racing to upgrade their models.
What’s New in Qwen 2.5-Max?
1. Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Architecture
Unlike traditional dense models, Qwen 2.5-Max uses 64 specialized "expert" networks activated dynamically via a gating mechanism. This allows efficient processing by only engaging relevant experts per task, reducing computational costs by 30% compared to monolithic models.
2. Unprecedented Training Scale
- 20+ trillion tokens: Trained on a curated dataset spanning academic papers, code repositories, and multilingual web content.
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Fine-tuned using 500,000+ human evaluations to improve safety and alignment.
3. Multimodal Mastery
Processes text, images, audio, and video with enhanced capabilities:
- Analyzes 20-minute videos for content summaries[5][42].
- Generates SVG code from visual descriptions.
- Supports 29 languages, including Chinese, English, and Arabic.
Key Differences vs. DeepSeek-V3
| Feature | Qwen 2.5-Max | DeepSeek-V3 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | MoE with 72B parameters | Dense model (exact size undisclosed) |
| Training Cost | $12M (estimated) | $6M (reported) |
| Benchmarks | 89.4 Arena-Hard vs. DeepSeek’s 85.5 | Superior coding efficiency |
| Access | Closed-source API; partial open-source components | Fully open-weight |
| Token Handling | 128K context + 8K generation | 32K context limit |
Qwen outperforms DeepSeek-V3 in critical benchmarks:
- Arena-Hard: 89.4 vs. 85.5 (human preference alignment)
- LiveCodeBench: 38.7 vs. 37.6 (coding tasks)
- GPQA-Diamond: 60.1 vs. 59.1 (complex QA)
However, DeepSeek retains advantages in cost efficiency and coding-specific optimizations.
Comparison to OpenAI’s GPT-4o
| Metric | Qwen 2.5-Max | GPT-4o |
|---|---|---|
| MMLU-Pro | 85.3 | 83.7 |
| LiveBench | 62.2 | 58.9 |
| Training Tokens | 20T | 13T (estimated) |
| Multilingual Support | 29 languages | 12 languages |
| API Cost | $10/M input tokens | $2.50/M input tokens |
While Qwen leads in raw benchmarks, GPT-4o maintains broader ecosystem integration and lower API costs.
Technical Breakthroughs
1. Structured Data Handling
Excels at parsing tables, JSON, and financial reports—critical for enterprise applications.
2. Long-Context Optimization
- 1M token models: Specialized variants process 256K context with 8K generation.
- Dynamic resolution: Adjusts video frame rates for efficient temporal analysis.
3. Self-Correction Mechanism
Identifies reasoning errors mid-task, improving accuracy on logic puzzles by 22%.
Practical Applications
- Healthcare: Automates medical record analysis and drug discovery research.
- Finance: Detects fraud patterns and generates investment reports.
- Content Creation: Produces SEO-optimized articles and video scripts.
- Developer Tools: Open-source 72B parameter model available on Hugging Face.
Challenges and Controversies
- Bias Risks: Training data may reflect cultural/linguistic biases.
- Surveillance Concerns: Alibaba’s history with Uyghur recognition tech raises ethical questions.
- API Costs: At $10/M input tokens, it’s 4x pricier than DeepSeek.
The Road Ahead
Alibaba plans quantum computing integration and 10+ additional languages by 2026. While Qwen 2.5-Max doesn’t fully dethrone DeepSeek’s cost efficiency or GPT-4’s creativity, it establishes China as a formidable AI innovator. As the industry shifts toward specialized MoE architectures, this model sets new expectations for multimodal reasoning and enterprise-scale deployment.
The AI race is no longer a sprint—it’s a marathon of architectural ingenuity and strategic resource allocation.
https://ift.tt/XsTpRGl
https://ift.tt/qjGaLXl
https://guptadeepak.com/content/images/2025/01/alibaba-qwen-chinese-new-year-gupadeepak-1.png
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/alibabas-qwen-25-max-the-ai-marathoner-outpacing-deepseek-and-catching-openais-shadow
Tuesday, 28 January 2025
Complete Guide to AI Tokens: Understanding Optimization and Cost Management

Tokens are the fundamental building blocks that power AI language models, serving as the currency of AI interactions. However, managing these tokens effectively requires a deep understanding of how they work, how they interact with context windows, and how they impact both the performance and cost of AI applications.
Think of tokens as the vocabulary units that AI models use to process and generate text. Just as we break down language into words and phrases, AI models break down text into tokens. These can range from single characters to common words or phrases. However, tokens aren't just about text processing – they're intricately connected to how AI models understand context, maintain conversation history, and generate responses.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about AI tokens, from basic concepts to advanced optimization strategies. We'll explore how tokens work within context windows, examine practical implementations in code generation, and discover methods for cost optimization. Whether you're building an AI coding assistant, implementing chat interfaces, or developing enterprise AI solutions, understanding these concepts is crucial for creating efficient and cost-effective AI applications.
Our journey will take us through several key areas:
- The fundamental nature of tokens and how different AI models handle them
- The crucial role of context windows in managing token usage
- Practical strategies for optimizing token consumption
- Real-world implementations, including a detailed look at AI coding assistants
- Advanced techniques for managing costs while maintaining performance
By understanding these interconnected concepts, you'll be better equipped to make informed decisions about AI implementation and optimization in your projects.
Token Counts Across Major AI Models
Different AI models use different tokenization approaches:
OpenAI GPT Models
- GPT-o1: 200K context window
- GPT-4o: 128K context window
- GPT-4: 8K/32K context window options
- GPT-3.5 Turbo: 16K context window
- Pricing: $0.01-0.03 per 1K tokens (varies by model)
Anthropic Claude
- Claude 3 Opus: 200K context window
- Claude 3 Sonnet: 200K context window
- Claude 3 Haiku: 200K context window
- Pricing: $0.015-0.03 per 1K tokens (varies by model)
Google Gemini
- Gemini 1.5 Flash: 1M context window
- Gemini 1.5 Pro: 2M context window
- Pricing: $0.00025-0.001 per 1K tokens (varies by model)
Mistral
- Mistral Large 24.11: 128K context window
- Mistral Small 24.09: 32K context window
- Pricing: $0.0002-0.001 per 1K tokens (varies by model)
DeepSeek
- DeepSeek-Chat: 64k context window
- DeepSeek-Reasoner: 64k context window
- Pricing: $0.014-0.14 per 1M tokens (varies by model)
Understanding Context Windows
The context window is one of the most crucial concepts in working with AI language models, yet it's often misunderstood. Think of the context window as the AI model's working memory – it's the amount of information the model can "see" and consider at any given time. This window is measured in tokens, and its size directly impacts both the model's capabilities and your token usage costs.
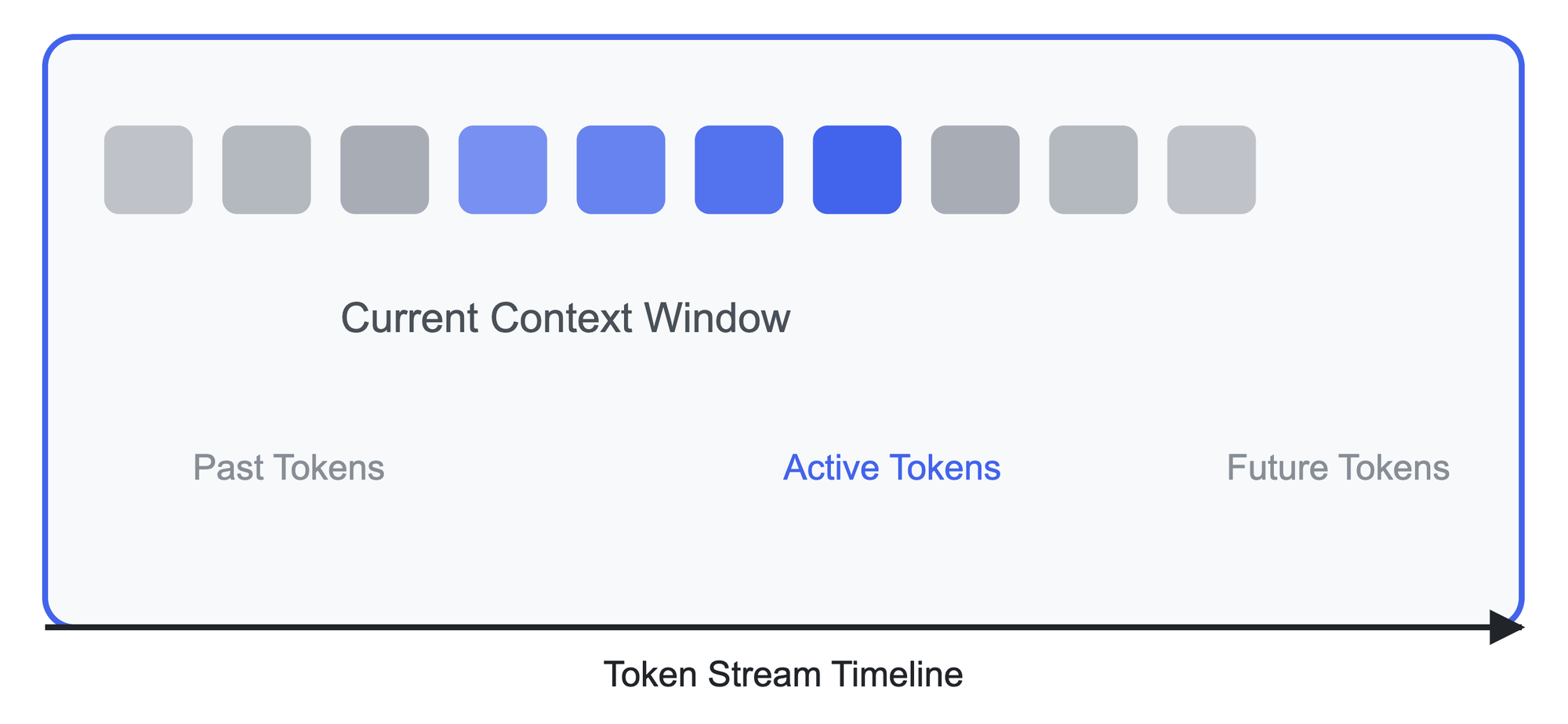
The Mechanics of Context Windows
A context window operates like a sliding glass through which the AI model views information. When you provide input to the model, this window encompasses both your prompt (input) and the space needed for the model's response (output). For instance, if you're using GPT-4 with a 32K context window, this means you have 32,000 tokens to work with in total – divided between your input and the expected output.
To better understand this concept, consider this analogy: Imagine you're reading a long document through a magnifying glass that can only show a certain number of words at once. The size of this magnifying glass is your context window. Just as you can't see words outside the magnifying glass's view, the AI model can't reference information that falls outside its context window.
Advanced Context Window Techniques
Several sophisticated techniques can help you maximize the effectiveness of your context window:
- Sliding Window Approach
The sliding window technique is particularly useful for processing long documents or conversations. Instead of trying to fit everything into one context window, you slide the window along the content, maintaining overlap for continuity:
def process_with_sliding_window(document, window_size=4000, overlap=1000): tokens = tokenize_document(document) results = [] for i in range(0, len(tokens), window_size - overlap): window = tokens[i:i + window_size] context = process_window(window) results.append(context) return merge_results(results)- Hierarchical Summarization
For very long contexts, implement a hierarchical summarization approach:
class HierarchicalContext: def manage_long_context(self, full_context): if count_tokens(full_context) > self.max_tokens: # Level 1: Create detailed summaries of chunks chunks = self.split_into_chunks(full_context) detailed_summaries = [self.summarize(chunk, 'detailed') for chunk in chunks] # Level 2: Create high-level summary of summaries if count_tokens(' '.join(detailed_summaries)) > self.max_tokens: return self.summarize(' '.join(detailed_summaries), 'high_level') return ' '.join(detailed_summaries) return full_contextBest Practices for Context Window Usage
When working with context windows, consider these essential practices:
- Content Prioritization
Not all content deserves equal space in your context window. Implement a priority system that considers:- Recency of information
- Relevance to the current task
- Importance of maintaining context continuity
- Dynamic Token Allocation
Allocate your token budget based on the specific requirements of your task:- Reserve more tokens for complex reasoning tasks
- Use fewer tokens for straightforward generation tasks
- Maintain a buffer for unexpected context needs
- Context Refreshing
Regularly refresh your context window to maintain relevance:
def refresh_context(self, current_context): # Remove outdated information refreshed_context = remove_outdated_info(current_context) # Compress remaining context if needed if count_tokens(refreshed_context) > self.max_tokens * 0.8: return self.compress_context(refreshed_context) return refreshed_contextImpact on Token Usage and Costs
Understanding the relationship between context windows and token usage is crucial for cost optimization. Here's how different context window sizes affect token usage and costs:
- Larger windows provide more context but increase token usage and costs
- Smaller windows are more cost-effective but may require more API calls
- Finding the optimal window size depends on your specific use case
Optimizing Token Usage
For Code Generation
Optimizing token usage for code generation requires a careful balance between providing sufficient context and maintaining efficiency. When working with AI models for code generation, the approach should focus on three key areas: prompt engineering, request structuring, and response management.
Effective prompt engineering begins with clarity and precision. Rather than providing lengthy explanations, developers should focus on crafting prompts that clearly define the desired outcome while minimizing token usage. This includes:
- Specifying the exact programming language and version requirements
- Defining the scope and functionality in clear, concise terms
- Including only relevant technical constraints and dependencies
Here's an example of an efficient request structure:
# Efficient request structure that minimizes tokens while maximizing clarity{ "task": "Create login function", "requirements": ["JWT", "password hashing"], "language": "Python"}Response handling is equally crucial for optimal token usage. Modern applications should implement streaming responses for larger code generations, which allows for progressive rendering and better user experience while managing token consumption. Additionally, implementing a robust caching system for commonly requested code patterns can significantly reduce token usage over time.
Best Practices for AI Code Generation
When implementing an AI coding assistant, consider these best practices:
- Context Relevance
Always prioritize the most relevant code context. This might include:- Direct dependencies of the code being generated
- Similar implementations in the codebase
- Related configuration and utility functions
- Token Efficiency
Implement efficient token usage strategies:- Use code embeddings to quickly identify relevant sections
- Maintain a cache of commonly used code patterns
- Implement intelligent context pruning for large codebases
- Quality Assurance
Ensure generated code maintains high quality:- Validate against project-specific style guides
- Check compatibility with existing code
- Verify security best practices are followed
This implementation demonstrates how to build an AI coding assistant that balances token efficiency with code quality, providing developers with helpful and contextually aware code generation capabilities.
For Internal Applications
When developing internal applications that leverage AI capabilities, document processing and conversation management become central concerns for token optimization. The approach to handling these aspects requires careful consideration of both technical implementation and practical usage patterns.
Document processing in AI-powered internal applications requires sophisticated chunking strategies. Rather than processing entire documents at once, which can quickly consume token quotas, developers should implement intelligent chunking mechanisms that break documents into meaningful segments while maintaining context. This can be achieved through:
- Semantic chunking that preserves the logical flow of information
- Overlapping windows that maintain context between chunks
- Embedding-based retrieval systems for efficient information access
Consider this example of efficient conversation management:
def manage_context(conversation_history): # Implement intelligent context retention return truncate_to_token_limit( filter_relevant_messages(conversation_history), max_tokens=4000 )For AI Agents
AI agents present unique challenges in token optimization due to their need to maintain context over extended interactions while remaining responsive and cost-effective. The key to successful token optimization in AI agents lies in sophisticated context management and efficient tool integration.
Context management for AI agents requires a hierarchical approach to memory and context retention. This involves implementing multiple layers of memory:
- Short-term memory for immediate context
- Medium-term memory for relevant recent interactions
- Long-term memory stored in vector databases for historical context
Here's an implementation example that demonstrates context compression:
class AIAgent: def compress_context(self): # Implement intelligent context summarization return generate_summary( self.conversation_history, max_tokens=500 )Best Practices for Cost Optimization
Cost optimization in AI applications requires a comprehensive approach that combines technical implementation with strategic decision-making. The foundation of effective cost optimization begins with accurate token counting and usage monitoring.
Implementing precise token counting mechanisms is essential for managing costs effectively:
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizerdef count_tokens(text): tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2') return len(tokenizer.encode(text))Beyond basic token counting, organizations should implement tiered processing strategies that match computational resources with task requirements. This involves creating a hierarchy of models and processing approaches:
- Using lightweight models for initial text processing and classification
- Reserving more powerful (and expensive) models for complex tasks
- Implementing sophisticated caching mechanisms to avoid redundant processing
Batch processing can significantly reduce costs by optimizing token usage across multiple requests:
def batch_process(items, batch_size=10): return [ process_batch(items[i:i+batch_size]) for i in range(0, len(items), batch_size) ]The final piece of cost optimization involves implementing robust monitoring and analytics systems. Organizations should:
- Track token usage patterns across different types of requests
- Analyze cost-per-request metrics to identify optimization opportunities
- Implement dynamic usage quotas based on business value and ROI
Advanced Token Optimization Techniques
1. Dynamic Model Selection
def select_model(task_complexity, input_length): if task_complexity == 'low' and input_length < 1000: return 'gpt-3.5-turbo' return 'gpt-4'2. Context Window Management
def manage_context_window(history, new_message): total_tokens = count_tokens(history + new_message) if total_tokens > MAX_TOKENS: return truncate_and_summarize(history) return history + new_message3. Hybrid Approaches
- Combine embedding searches with direct queries
- Use cached responses for common queries
- Implement progressive enhancement
Conclusion: Mastering Token Usage for Optimal AI Implementation
Understanding and optimizing token usage is more than just a technical requirement – it's a fundamental skill for anyone working with AI language models. Throughout this guide, we've explored how tokens form the foundation of AI interactions and how their effective management can dramatically impact both performance and costs.
The relationship between tokens and context windows proves particularly crucial. As we've seen in our detailed exploration, the context window acts as the AI's working memory, determining how much information it can process at once. This understanding becomes especially valuable when implementing practical applications like AI coding assistants, where managing context effectively can mean the difference between generating precise, contextually aware code and producing disconnected, less useful output.
Understanding Token Fundamentals:
- Tokens serve as the basic units of AI processing, breaking down text into manageable pieces
- Different models handle tokens differently, with varying costs and context window sizes
- Token optimization requires balancing context preservation with cost efficiency
Context Window Management:
- Context windows determine the scope of what AI models can "see" and process
- Effective context window management requires strategic approaches to information organization
- Sliding windows and hierarchical summarization provide powerful tools for handling long contexts
Practical Applications:
- AI coding assistants demonstrate how token management translates into real-world applications
- Strategic context prioritization ensures optimal use of available tokens
- Streaming implementations help manage large-scale generations efficiently
Cost Optimization Strategies:
- Token usage directly impacts costs, making optimization crucial for scalability
- Implementing tiered processing helps balance cost with performance
- Monitoring and analytics provide insights for continuous optimization
Looking ahead, AI continues to evolve, with models becoming more sophisticated and context windows growing larger. However, the fundamental principles of token management and optimization remain crucial. By understanding these concepts and implementing the strategies we've discussed, you can build more efficient, cost-effective AI applications that make the most of available resources.
Remember that effective token management is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring, optimization, and adjustment of your token usage strategies will help ensure your AI applications remain both powerful and cost-effective as your needs evolve and grow.
Whether you're implementing an AI coding assistant, building enterprise applications, or developing new AI-powered tools, the principles and strategies outlined in this guide provide a foundation for successful token management. By applying these concepts thoughtfully and systematically, you can create AI applications that not only perform well but do so efficiently and economically.
https://ift.tt/09cME3n
https://ift.tt/zvIw1aH
https://guptadeepak.com/content/images/2025/01/AI-token-guide-Understand-token-context.png
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/complete-guide-to-ai-tokens-understanding-optimization-and-cost-management
Sunday, 26 January 2025
The Small Business Guide to Everyday Access Management and Secure Off-boarding

In our previous articles, we explored the potentially devastating costs of poor access management and laid out the foundation for building a robust access management system. Now, let's focus on the day-to-day practices that keep your business secure. Think of this as your playbook for maintaining digital security without letting it consume your workday.
Daily Access Management: Creating Security Habits That Stick
Managing access to your company's digital resources is much like running a well-organized restaurant. Just as a restaurant manager needs to know who's handling food prep, managing the register, and serving customers, you need clear systems for managing digital access. The key is establishing routines that become as natural as locking your doors at night.
The 10-Minute Morning Security Routine
Start each workday with a quick but thorough security check. Think of it as your business's digital vital signs check – a structured way to spot potential issues before they become problems.
First 3 Minutes: Authentication Review
Begin by examining your authentication logs. You're not just looking at numbers; you're searching for patterns that might indicate security concerns. For example:
- Multiple failed login attempts followed by a successful login could suggest a breach
- Login attempts from unusual locations might indicate unauthorized access attempts
- Access patterns outside normal business hours could reveal compromised credentials
When reviewing these logs, think like a detective. A single failed login might be a typo, but five failed attempts from different countries should raise red flags.
Next 2 Minutes: System Health Check
Just as a doctor checks vital signs during a physical, your systems need regular health monitoring. Look for:
- Unusual CPU or memory usage that might indicate security issues
- Unexpected network traffic patterns that could suggest data exfiltration
- Backup system status to ensure your safety net is functional
- Security tool updates or warnings that need attention
Don't just confirm systems are running – verify they're running correctly. A system running at 100% CPU at 3 AM might be doing important work, or it might be mining cryptocurrency for an attacker.
Final 5 Minutes: Access Request Management
Process access requests with a security-first mindset. For each request, consider:
- Does this person truly need this level of access to perform their role?
- Could a more limited permission set accomplish the same goal?
- Are there any risks associated with granting this access?
- How will we monitor and review this access going forward?
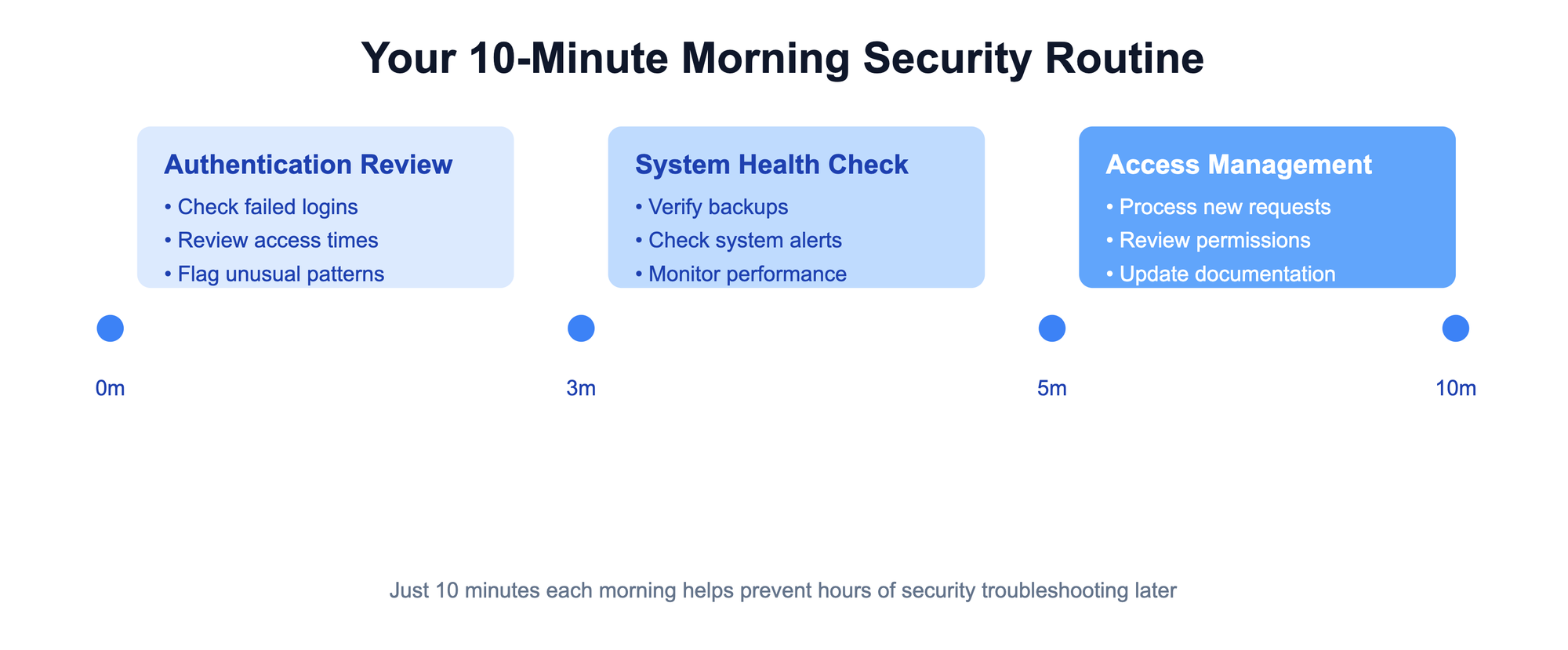
Remember, every access grant is a potential security risk. The goal is to provide enough access for people to do their jobs effectively while minimizing potential vulnerabilities.
Responding to Access Issues: The 3-Minute Protocol
When access issues arise, you need a response that's both quick and secure. Here's how to handle common access problems efficiently:
Minute 1: Verification
Start with thorough verification, but make it efficient:
- Confirm the requester's identity through established channels
- Verify their authorization level for the requested access
- Check if the request aligns with their role and responsibilities
Think of this like checking ID at a secure facility – it might take a moment, but it's essential for security.
Minute 2: Implementation
Execute the necessary changes with precision:
- Make the required access adjustments
- Document the changes in your system
- Set any necessary time limits or review dates
Minute 3: Confirmation and Documentation
Wrap up the process professionally:
- Confirm the changes work as intended
- Notify relevant team members
- Update your access management records
Secure Offboarding: Protecting Your Business When Employees Leave
Employee departures represent one of the most significant security risks for small businesses. Consider this scenario: A marketing agency discovered a former employee still had access to their client presentation files three months after leaving. This wasn't malicious – it was simply overlooked in a rushed offboarding process.
Understanding the Scope of Modern Access
Today's employees typically have access to dozens of systems:
Let's understand how deep this access typically goes. A modern employee might have their digital fingerprints across:
- Email and communication platforms where they've exchanged sensitive information
- Project management tools containing strategic plans and timelines
- Cloud storage services holding company documents
- Social media accounts representing your brand
- (CRM) Customer relationship management systems with valuable client data
- Financial software with sensitive transaction records
- Development and deployment tools containing intellectual property
Each of these access points needs careful attention during offboarding. Think of it like collecting keys from a departing property manager – you need to know about every lock they had access to.
The Two-Week Offboarding Process
When you have advance notice of an employee's departure, follow this comprehensive process:
Week 1: Documentation and Knowledge Transfer
Days 1-2: Complete Access Mapping
- Document every system the employee has access to
- List all projects and responsibilities
- Identify critical knowledge that needs to be transferred
Days 3-5: Knowledge Preservation
- Schedule detailed handover meetings
- Document unique processes and procedures
- Update team documentation
- Ensure critical information isn't lost
Week 2: Access Management and Security
Days 6-8: Gradual Access Reduction
- Remove unnecessary access rights
- Monitor activity for any concerns
- Transfer ownership of shared accounts
- Begin archiving important communications
Days 9-10: Final Preparations
- Complete the offboarding checklist
- Conduct exit interviews
- Prepare for final account termination
- Document any remaining tasks or responsibilities
Emergency Offboarding: The 15-Minute Protocol
Sometimes you don't have the luxury of a two-week notice. Here's your rapid response plan:
First 5 Minutes: Critical System Protection
- Disable primary account access
- Revoke VPN and remote access capabilities
- Lock access to cloud services and sensitive data
- Reset critical shared passwords
Next 5 Minutes: Communication Systems
- Remove email access and set up forwards
- Disable chat and collaboration tool access
- Remove from project management systems
Final 5 Minutes: Documentation and Notification
- Document all actions taken
- Notify relevant team members
- Begin comprehensive access audit
Building Security into Your Daily Operations
The key to effective access management is making it part of your regular business rhythm. Here are five essential habits to develop:
1. Weekly Access Reviews
Every Friday, spend 15 minutes reviewing:
- Active user accounts and their current access levels
- Temporary access that should be revoked
- Unused licenses that could be reallocated
- Any unusual patterns in system access logs
2. Monthly Security Assessments
Once a month, conduct a deeper review:
- Evaluate access patterns across all systems
- Update documentation of security procedures
- Review and adjust access policies as needed
- Check for any unnecessary standing permissions
3. Quarterly Permission Audits
Every three months, perform a comprehensive audit:
- Review all user access rights
- Clean up outdated permissions
- Update security documentation
- Assess the effectiveness of current procedures
4. Continuous Training and Awareness
Make security awareness an ongoing process:
- Share monthly security tips with your team
- Review recent security incidents and lessons learned
- Update team members on new security procedures
- Encourage reporting of security concerns
Practical Implementation Steps
Start implementing these practices today:
- Create Your Access Inventory
- Map out all your systems and who has access
- Document current permission levels
- Identify system owners and administrators
- Note any temporary or special access arrangements
- Establish Basic Procedures
- Create standard forms for access requests
- Document your emergency response procedures
- Set up regular review schedules
- Develop your offboarding checklist
- Set Up Monitoring Systems
- Enable logging on all critical systems
- Configure basic security alerts
- Document your review process
- Create response procedures for common issues
Conclusion
Effective access management doesn't require complex systems or constant attention. By establishing clear procedures and maintaining consistent habits, you can protect your business while keeping operations smooth and efficient. Start with these fundamentals and gradually improve your processes as your company grows.
Remember: Security isn't about having the most sophisticated tools – it's about consistently following simple, effective practices that protect your business assets.
This article is part of a comprehensive guide on access management for small businesses. Stay tuned for our upcoming ebook that will provide detailed implementation guides, templates, and best practices for securing your business effectively.
https://ift.tt/ubIAK7E
https://ift.tt/OAWBl6h
https://guptadeepak.com/content/images/2025/01/The-Small-Business-Guide-to-Everyday-Access-Management-and-Secure-Offboarding.png
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/the-small-business-guide-to-everyday-access-management-and-secure-off-boarding
Saturday, 25 January 2025
DeepSeek: Revolutionizing AI with Efficiency Innovation and Affordability

DeepSeek, developed by the Chinese AI research team under the umbrella of the quantitative investment firm Huanfang, represents a paradigm shift in large language models (LLMs). Combining cutting-edge architectural innovations with cost-effective training strategies, DeepSeek challenges industry giants like OpenAI and Anthropic by delivering state-of-the-art performance at a fraction of the cost. This article explores DeepSeek’s internal architecture, its efficiency advantages, and the factors enabling its affordability, while contextualizing its impact on the AI landscape.
What is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek is a family of open-source and proprietary LLMs designed for high performance across diverse tasks, including code generation, mathematical reasoning, and multilingual processing. The latest iteration, DeepSeek V3, is a 671-billion-parameter Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that activates only 37 billion parameters per token, optimizing computational efficiency without sacrificing capability.
Key milestones include:
- Open-Source Accessibility: Released under MIT licensing, DeepSeek models are freely available for customization, fostering community-driven innovation.
- Performance Benchmarks: Outperforms competitors like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet in coding (HumanEval-Mul: 82.6%) and mathematics (MATH-500: 90.2%).
- Cost Leadership: Input costs as low as $0.14 per million tokens (cache miss) and $0.014 per million tokens (cache hit), making it 96% cheaper than GPT-4o.
Architectural Innovations Behind DeepSeek’s Speed and Efficiency
DeepSeek’s breakthrough performance stems from a suite of cutting-edge architectural advancements that optimize computational efficiency while maintaining high accuracy.
Here are the key innovations driving its speed and resource efficiency:
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Architecture
DeepSeek’s MoE design divides the model into specialized subnetworks (“experts”) activated dynamically per token. This approach minimizes computational load while maximizing parameter utilization:
- Dynamic Routing: Each token selects 8 out of 256 routing experts per MoE layer, ensuring task-specific processing.
- Shared and Routed Experts: A hybrid of shared experts (providing general knowledge) and routed experts (specializing in specific features) balances stability and specialization.
- Auxiliary-Loss-Free Load Balancing: Unlike traditional MoE models, DeepSeek uses dynamic bias adjustments to distribute workloads across experts, avoiding performance degradation from auxiliary losses.
Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA)
MLA optimizes attention mechanisms by compressing key-value (KV) vectors into low-rank latent spaces, reducing memory usage and accelerating inference:
- Low-Rank Compression: Compresses KV vectors to 1/16th their original size, slashing GPU memory requirements.
- Efficient Caching: Stores compressed latent vectors during inference, enabling faster token generation.
Multi-Token Prediction (MTP)
DeepSeek V3 predicts multiple tokens sequentially during training, enhancing both efficiency and coherence:
- Denser Training Signals: MTP increases training data utilization, improving model accuracy on long-context tasks.
- Speculative Decoding: During inference, MTP allows parallel token prediction, accelerating response times.
FP8 Mixed Precision Training
DeepSeek’s adoption of 8-bit floating-point (FP8) precision reduces GPU memory usage and computational costs:
- Memory Savings: FP8 halves memory consumption compared to FP16, enabling training on fewer GPUs.
- Training Stability: Fine-grained quantization ensures numerical stability, achieving a training cost of $5.576 million—10x cheaper than comparable models.
Why is DeepSeek Faster Than OpenAI ChatGPT?
DeepSeek achieves superior speed through architectural and operational innovations. Its Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) design dynamically activates only 37 billion parameters per token (vs. ChatGPT’s dense activation of all parameters), slashing computational waste. Multi-Head Latent Attention compresses key-value vectors to 1/16th their size, accelerating memory-heavy attention mechanisms, while FP8 mixed precision training reduces GPU memory demands by 50%.
During inference, DeepSeek decouples context pre-processing from token generation, minimizing latency, and uses hardware co-design—like overlapping computation/communication phases—to eliminate bottlenecks. Though ChatGPT excels in raw token throughput, DeepSeek’s leaner architecture and optimized resource allocation deliver faster, cost-effective performance for real-world applications.
Optimized Inference Pipeline
- Prefilling-Decoding Separation: DeepSeek decouples context pre-processing from token generation, minimizing latency during interactive tasks.
- Redundant Expert Hosting: Critical experts are duplicated across GPUs, reducing communication overhead in distributed systems.
Hardware and Framework Co-Design
- DualPipe Algorithm: Overlaps computation and communication phases in pipeline parallelism, achieving near-zero “pipeline bubbles”.
- Efficient Communication Kernels: Leverages InfiniBand and NVLink bandwidth for fast cross-node data transfer.
Benchmark Comparisons
| Metric | DeepSeek V3 | GPT-4o | Claude 3.5 Sonnet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tokens/sec (Output) | 14.2 | 53.6 | 71.7 |
| Latency (TTFT) | 0.96s | 0.70s | 1.01s |
| Context Window | 128K tokens | 128K tokens | 200K tokens |
While OpenAI’s GPT-4o excels in raw token speed, DeepSeek’s latency and cost-efficiency make it preferable for budget-sensitive applications.
Why is DeepSeek So Affordable?
Cost-Efficient Training Strategies
- FP8 Precision: Reduces GPU hours by 40%, cutting pre-training costs to 2.788 million H800 GPU hours.
- Knowledge Distillation: Smaller models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B) inherit capabilities from the flagship model, lowering deployment costs.
Open-Source Ecosystem
- Community Contributions: Open weights and modular designs allow developers to optimize inference locally, avoiding API fees.
- Distilled Variants: Lightweight models like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B offer near-flagship performance at 1/10th the cost.
Strategic Pricing Model
| Model | Input Cost (per million tokens) | Output Cost (per million tokens) |
|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek V3 | $0.14 (cache miss) | $0.28 |
| GPT-4o | $2.50 (cache miss) | $10.00 |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | $3.00 | $15.00 |
DeepSeek’s cache-hit pricing ($0.014/million tokens) and optimized resource allocation enable unparalleled cost savings.
Real-World Applications and Limitations
Use Cases
- Coding Assistants: Achieves 82.6% accuracy on LiveCodeBench, surpassing GPT-4o (80.5%)
- Educational Tools: Scores 88.5% on MMLU, rivaling Claude 3.5 Sonnet (88.3%)
- Multilingual Systems: Excels in Chinese benchmarks (C-Eval: 86.5%), making it ideal for global enterprises
Limitations
- Context Window: 128K tokens vs. Claude 3.5 Sonnet’s 200K
- Multimodal Gaps: Lacks native image-processing capabilities compared to Llama 3.2 Vision
Shift in AI Innovation
DeepSeek’s rise underscores a critical shift in AI development: innovation need not be tethered to exorbitant budgets. Through architectural ingenuity—MoE with dynamic routing, FP8 training, and open-source collaboration—DeepSeek delivers GPT-4-level performance at 1/20th the cost. While challenges like context length and multimodality remain, its affordability and efficiency position it as a transformative force in democratizing AI. As the industry evolves, DeepSeek’s blueprint offers a compelling alternative to proprietary models, proving that agility and creativity can rival financial might.
https://ift.tt/YXfGK1y
https://ift.tt/CdY8HmM
https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1677756119517-756a188d2d94?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDN8fEFJfGVufDB8fHx8MTczNzgzMDM4Mnww&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=80&w=2000
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/deepseek-revolutionizing-ai-with-efficiency-innovation-and-affordability
Friday, 24 January 2025
How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Software: A Comprehensive Guide

Imagine walking into your office one morning to find that all your company's data has been encrypted by ransomware, or discovering that your customers' sensitive information has been exposed in a data breach. These aren't just hypothetical scenarios—they're real nightmares that businesses face every day. In fact, as I write this guide, another organization somewhere in the world is dealing with a cybersecurity crisis that could have been prevented with the right security tools and practices.
I've spent years helping organizations navigate the complex world of cybersecurity, and I've seen firsthand how the right security choices can mean the difference between a minor incident and a catastrophic breach. This guide isn't just another technical manual—it's a practical roadmap born from real-world experience, successes, and yes, even failures.
Think of cybersecurity software like the security system for your home. Just as you wouldn't protect your house with just a simple lock when you have valuable possessions inside, you can't protect your organization's digital assets with basic security measures alone. But with so many options available, how do you know which security tools are right for your organization?
Why This Guide Matters
Every day, I meet business leaders who feel overwhelmed by cybersecurity decisions. They know they need protection, but they're drowning in technical jargon, conflicting advice, and countless product options. If you're feeling this way, you're not alone. A recent study showed that 82% of business leaders feel uncertain about their cybersecurity choices, even as cyber threats continue to evolve and multiply.
This uncertainty comes at a cost. In 2024, organizations worldwide lost an average of $4.45 million per data breach. But here's the most striking part: 76% of these breaches could have been prevented with the right security tools and practices. This isn't just about protecting against losses—it's about enabling your business to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
What You'll Learn
Throughout this guide, we'll cut through the complexity and confusion surrounding cybersecurity software selection. We'll explore:
The evolving landscape of cyber threats and why traditional security measures no longer suffice in today's digital world. You'll understand not just what threats exist, but how they could specifically impact your organization.
How to assess your organization's unique security needs, whether you're a small business just starting your security journey or a large enterprise looking to enhance your existing security posture. We'll walk through practical assessment methods that help you identify your most critical security requirements.
The various types of cybersecurity software available and how they work together to create a comprehensive security strategy. Rather than overwhelming you with technical details, we'll focus on understanding how each tool contributes to your overall security.
A structured approach to evaluating and selecting security vendors, with real-world examples of what works—and what doesn't. You'll learn how to look beyond flashy features to find solutions that truly meet your needs.
Practical strategies for implementing and maintaining your chosen security solutions. We'll cover everything from initial deployment to long-term maintenance, with a focus on sustainable security practices.
A Personal Note
As someone who has built and scaled security solutions for organizations worldwide, I understand the challenges you face. I've seen small businesses recover from devastating cyber attacks, and I've helped large enterprises transform their security posture. But I've also seen organizations struggle with poorly chosen or badly implemented security tools.
This guide reflects not just my personal experience, but the collective wisdom of countless security professionals and organizations that have faced and overcome cybersecurity challenges. Throughout these pages, you'll find practical advice, real-world examples, and proven strategies that you can apply to your own organization.
Remember, choosing the right cybersecurity software isn't just about selecting tools—it's about protecting your organization's future. Whether you're a small business owner worried about ransomware, a technology leader planning your security strategy, or a security professional looking to enhance your organization's defenses, this guide will help you make informed decisions about your cybersecurity investments.
Let's begin this journey together, starting with understanding the current cybersecurity landscape and the threats your organization faces in today's digital world.
The Rise of Cybersecurity Threats
The cybersecurity landscape has transformed dramatically in recent years, presenting unprecedented challenges for organizations worldwide. In 2023 and early 2024, we've witnessed a significant evolution in attack sophistication and frequency, with several key trends emerging that shape our current threat landscape.
AI-Powered Attacks
The democratization of AI has led to more sophisticated attack vectors. Cybercriminals now leverage AI to:
- Generate convincing phishing emails that bypass traditional filters
- Create deepfake voice and video content for social engineering
- Automate attack patterns and exploit vulnerability discovery
- Develop polymorphic malware that evades detection
Ransomware Evolution
Ransomware attacks have become more targeted and devastating. Recent statistics show:
- A 500% increase in ransomware attacks targeting critical infrastructure
- Average ransom demands exceeding $1.5 million in 2024
- Double extortion tactics affecting 82% of ransomware cases
- Healthcare sector experiencing a 74% increase in ransomware incidents
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Supply chain attacks have emerged as a critical concern:
- 60% of organizations experienced a supply chain-related breach in 2024
- Third-party software vulnerabilities contributed to 43% of data breaches
- Cloud service provider attacks affected millions of downstream customers
- Open-source software vulnerabilities increased by 42% year-over-year
The Real Cost of Cyberattacks
The financial impact of cybersecurity breaches has reached historic levels, with various industries experiencing unprecedented losses.
Direct Financial Impact
Recent studies reveal alarming statistics:
- Average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million in 2024
- Ransomware recovery costs averaged $1.85 million per incident
- Cybersecurity insurance premiums increased by 28% in 2024
- Small businesses faced average costs of $149,000 per incident
Industry-Specific Impacts
Healthcare Sector:
- Patient data breaches affected 87 million records in 2024
- Average cost per compromised record: $408
- 89% of healthcare organizations experienced a cybersecurity incident
- Recovery time averaged 287 days
Financial Services:
- Banking trojans increased by 92% in 2024
- Average cost per incident: $5.72 million
- 23% increase in mobile banking malware
- 68% of financial institutions reported increased attack sophistication
Manufacturing:
- Operational technology (OT) attacks increased by 87%
- Production downtime costs averaged $5 million per incident
- Industrial IoT vulnerabilities rose by 46%
- Supply chain disruptions affected 72% of manufacturers
Reputational and Long-term Impact
Beyond immediate financial losses, organizations face:
- Customer churn rates increasing by 3.5% after major breaches
- Brand value depreciation averaging 21% post-incident
- Regulatory fines under GDPR reaching €1.6 billion in 2024
- Legal settlements averaging $64 million for class-action lawsuits
Emerging Threat Vectors
Cloud Security Challenges
As organizations accelerate cloud adoption:
- Misconfigured cloud services caused 43% of data breaches
- Container vulnerabilities increased by 154%
- Serverless function attacks rose by 78%
- Multi-cloud environments increased attack surface by 67%
IoT Vulnerabilities
The expanding IoT landscape presents new risks:
- 67% of IoT devices contain critical vulnerabilities
- Botnet attacks increased by 235% in 2024
- Smart device exploits rose by 122%
- Industrial IoT attacks caused $8.5 billion in damages
Remote Work Security
Distributed workforce challenges include:
- 94% increase in VPN exploitation attempts
- Home network compromises affecting corporate data
- 89% rise in endpoint security incidents
- Shadow IT increasing security risks by 42%
Why Traditional Security Measures Aren't Enough
The conventional security approach has become obsolete due to:
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Modern APTs demonstrate:
- Average dwell time of 287 days before detection
- Sophisticated evasion techniques bypassing traditional security
- State-sponsored attacks increasing by 48%
- Multi-stage attacks combining multiple threat vectors
Zero-Day Exploits
The landscape of unknown vulnerabilities:
- 66% increase in zero-day exploits in 2024
- Average patch deployment time: 97 days
- Zero-day exploit prices reaching $2.5 million
- 38% of breaches utilizing unknown vulnerabilities
AI and Machine Learning Requirements
Modern security demands:
- Real-time threat detection and response
- Behavioral analysis and anomaly detection
- Automated incident response capabilities
- Predictive threat intelligence
The Path Forward
Organizations must adopt a comprehensive security approach that includes:
- Zero Trust Architecture implementation
- AI-powered security solutions
- Continuous security monitoring and assessment
- Employee security awareness and training
- Regular third-party security audits
This evolving threat landscape requires a dynamic and proactive security strategy that goes beyond traditional measures, incorporating advanced technologies and methodologies to protect against sophisticated modern threats.
Understanding Your Security Needs
The Critical Importance of Security for Small Businesses
Many small business owners believe they're too small to be targeted by cybercriminals. However, recent statistics tell a different story. Small businesses have become increasingly attractive targets precisely because they often lack robust security measures. In 2024, 43% of all cyber attacks targeted small businesses, yet only 14% were adequately prepared to defend themselves.
The impacts on small businesses are particularly severe:
- 60% of small businesses close within six months of a cyber attack
- The average cost of a small business data breach reached $149,000 in 2024
- 83% of small businesses lack the funds to recover from a cyber attack
- Customer trust loss affects 89% of small businesses post-breach
Understanding the Stakes
Small businesses face unique challenges in cybersecurity because they often:
- Hold valuable customer and business data
- Serve as entry points to larger business networks
- Have limited IT resources and expertise
- Balance security needs with operational costs
Consider the case of Main Street Boutique, a small retail business that suffered a point-of-sale system breach in 2023. The incident resulted in:
- Theft of 3,000 customer credit card details
- $120,000 in direct costs for incident response
- 32% decrease in sales over the following quarter
- Loss of their payment processor relationship
Conducting a Comprehensive Security Assessment
A thorough security assessment helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Here's how to approach it systematically:
1. Asset Inventory and Classification
Start by documenting everything your business needs to protect:
Digital Assets:
- Customer databases and records
- Financial information and transaction data
- Intellectual property and trade secrets
- Email systems and communication platforms
- Website and e-commerce systems
- Cloud storage and applications
Physical Assets:
- Computers and mobile devices
- Network equipment and servers
- Point-of-sale systems
- Security cameras and IoT devices
- Backup systems and storage devices
Data Classification:
- Highly sensitive (customer financial data, healthcare records)
- Confidential (employee records, business plans)
- Internal use (operational procedures, training materials)
- Public (marketing materials, public website content)
2. Risk Assessment Framework
Implement a structured approach to identifying risks:
External Threats:
- Phishing and social engineering attempts
- Ransomware and malware attacks
- Data theft and unauthorized access
- DDoS attacks and service disruption
- Supply chain compromises
Internal Risks:
- Employee mistakes and negligence
- Unauthorized data access or sharing
- Lost or stolen devices
- Insufficient access controls
- Poor password practices
Vulnerability Assessment:
- Network security gaps
- Software update status
- Access control weaknesses
- Data backup vulnerabilities
- Physical security issues
3. Impact Analysis
Evaluate potential consequences across different areas:
Financial Impact:
- Direct costs of incident response
- Revenue loss from business disruption
- Legal and regulatory fines
- Customer compensation costs
- Insurance premium increases
Operational Impact:
- System downtime and productivity loss
- Data recovery time and effort
- Business process disruption
- Supply chain interruptions
- Employee morale and turnover
Reputational Impact:
- Customer trust erosion
- Brand damage
- Lost business opportunities
- Media coverage and public perception
- Partner relationship strain
Defining Security Objectives
Set clear, achievable security goals aligned with your business needs:
1. Core Security Objectives
Protect Critical Assets:
- Implement multi-layer data protection
- Secure customer information
- Protect intellectual property
- Safeguard financial data
- Maintain system integrity
Ensure Business Continuity:
- Minimize downtime risk
- Establish incident response procedures
- Create disaster recovery plans
- Maintain data backups
- Enable quick system recovery
Meet Compliance Requirements:
- Industry-specific regulations (SOC2, ISO, HIPAA, PCI DSS)
- Data protection laws (GDPR, CCPA)
- Industry standards and best practices
- Contractual obligations
- Insurance requirements
2. Operational Security Goals
Employee Security:
- Regular security awareness training
- Clear security policies and procedures
- Incident reporting mechanisms
- Access control protocols
- Mobile device management
Technical Security:
- Regular security updates and patches
- Network monitoring and protection
- Endpoint security measures
- Email and web filtering
- Encryption implementation
3. Growth-Oriented Security Planning
Future-Proofing:
- Scalable security solutions
- Flexible security architecture
- Technology adoption readiness
- Integration capabilities
- Cost-effective expansion options
Building a Security-First Culture
Create an environment where security becomes second nature:
Employee Engagement:
- Regular security updates and briefings
- Recognition for security-conscious behavior
- Clear incident reporting procedures
- Open communication channels
- Feedback incorporation
Training and Development:
- Monthly security awareness sessions
- Simulated phishing exercises
- Hands-on security tools training
- Role-specific security guidance
- Security certification support
Measuring Security Progress
Establish metrics to track security program effectiveness:
Security Metrics:
- Number of security incidents
- Time to detect and respond
- Employee training completion rates
- Security assessment scores
- Policy compliance levels
Business Impact Metrics:
- Security investment ROI
- Incident response costs
- Downtime reduction
- Customer trust indicators
- Compliance achievement
Remember, security is not a one-time effort but a continuous process of evaluation, implementation, and improvement. Even small businesses must prioritize security to protect their assets, customers, and future growth potential.
Exploring Cybersecurity Software Options
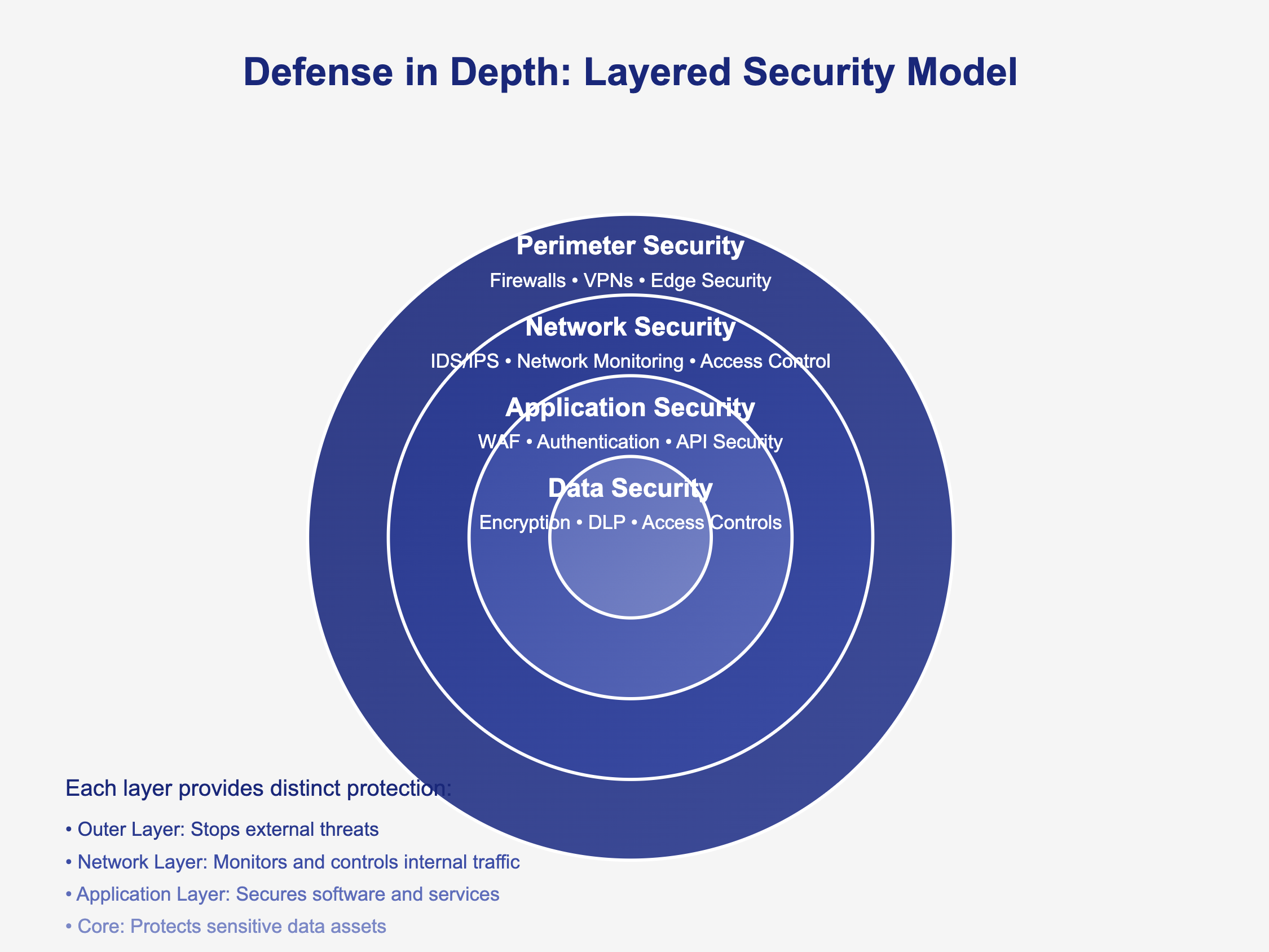
Understanding the Modern Security Software Ecosystem
The cybersecurity software landscape has evolved significantly from the days when a simple antivirus program was sufficient protection. Today's interconnected business environment requires a sophisticated yet manageable approach to security software. Organizations need to understand not just individual tools, but how these tools work together to create a comprehensive security posture.
Core Security Components
1. Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP)
Modern endpoint protection has evolved far beyond traditional antivirus capabilities. Today's EPP solutions serve as the first line of defense against a wide range of threats.
Why You Need It:
- Endpoints are the primary attack surface for 68% of security breaches
- Remote work has increased endpoint vulnerabilities by 42%
- Malware attacks increased by 358% in 2024
- 70% of successful breaches start at endpoints
Key Benefits:
- Real-time threat prevention and detection
- Reduced incident response time
- Centralized endpoint management
- Improved visibility into endpoint activities
Recommended Solutions:
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Best for enterprise-level protection
- SentinelOne: Excellent AI-powered protection
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Strong integration with Windows
- Sophos Intercept X: Great for small to medium businesses
Integration Tip: Look for EPP solutions that offer APIs for integration with your SIEM and security orchestration tools. This enables automated response workflows and centralized monitoring.
2. Network Security Solutions
Network security forms the backbone of your defense strategy, protecting data in transit and controlling access to resources.
Why You Need It:
- Network attacks increased by 67% in 2024
- 43% of breaches involve network vulnerabilities
- Remote work has expanded network attack surfaces
- Cloud adoption requires enhanced network security
Key Benefits:
- Comprehensive traffic monitoring
- Threat prevention at network level
- Secure remote access
- Network segmentation capabilities
Essential Components:
a) Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW):
- Palo Alto Networks
- Fortinet FortiGate
- Cisco Firepower
- Check Point
b) Network Detection and Response (NDR):
- Darktrace
- ExtraHop
- Vectra AI
- Cisco Secure Network Analytics
Integration Tip: Choose solutions that support common standards like STIX/TAXII for threat intelligence sharing and Syslog for log aggregation.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM has become crucial as organizations move towards zero trust security models.
Why You Need It:
- 61% of breaches involve stolen credentials
- Password attacks increased by 74% in 2024
- Remote work requires robust access control
- Compliance regulations mandate strong authentication
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced security through strong authentication
- Reduced risk of credential theft
- Improved user experience
- Simplified compliance
Recommended Solutions:
- Okta: Best for cloud-first organizations
- Microsoft Azure AD: Strong Microsoft ecosystem integration
- OneLogin: Great for hybrid environments
- Ping Identity: Excellent for enterprise needs
Integration Tip: Ensure your IAM solution can integrate with your HR systems for automated user provisioning and deprovisioning.
4. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems provide centralized visibility and analysis of security events across your infrastructure.
Why You Need It:
- Organizations face an average of 10,000 alerts daily
- Manual analysis of security events is impossible
- Compliance requirements mandate log monitoring
- Threat detection requires contextual analysis
Key Benefits:
- Centralized security monitoring
- Automated alert correlation
- Compliance reporting
- Incident response coordination
Recommended Solutions:
- Splunk Enterprise Security
- IBM QRadar
- Exabeam
- Microsoft Sentinel
Integration Tip: Your SIEM should be the central hub of your security operations, integrating with all other security tools for comprehensive visibility.
Creating an Integrated Security Stack
The key to effective security software implementation is integration. Here's how to build a connected security ecosystem:
1. Integration Framework
Build your security stack around these principles:
- Common data format for sharing information
- Standardized APIs for tool communication
- Centralized management and monitoring
- Automated workflow capabilities
2. Integration Levels
Implement integration in phases:
- Basic: Log aggregation and alert forwarding
- Intermediate: Bi-directional data sharing and automated responses
- Advanced: Full orchestration and automated workflows
3. Essential Integrations
Core Connections:
- EPP → SIEM: For endpoint event monitoring
- IAM → EPP: For identity-based access control
- NDR → SIEM: For network threat detection
- All → SOAR: For automated response
Simplifying Your Security Stack
While comprehensive security is essential, complexity can be the enemy of effectiveness. Here's how to keep your security stack manageable:
1. Consolidation Strategies
Reduce Tool Sprawl:
- Choose platforms with multiple capabilities
- Prioritize integrated solutions over point products
- Focus on core functionalities
- Remove redundant tools
2. Operational Efficiency
Streamline Management:
- Implement centralized management consoles
- Automate routine tasks
- Standardize policies across tools
- Use integrated reporting
3. Cost Optimization
Maximize Value:
- Evaluate tool usage and effectiveness
- Consider consolidated licensing
- Remove underutilized features
- Focus on ROI metrics
Future-Proofing Your Security Stack
As technology evolves, your security stack should be ready to adapt:
1. Scalability Considerations
Plan for Growth:
- Choose tools that scale with your business
- Consider cloud-based solutions
- Plan for increased data volumes
- Account for new technology adoption
2. Emerging Technologies
Prepare for the Future:
- AI and machine learning capabilities
- Zero trust architecture support
- Cloud-native security features
- IoT security requirements
Measuring Success
Monitor these key metrics to ensure your security stack is effective:
1. Security Metrics
Track Performance:
- Mean time to detect (MTTD)
- Mean time to respond (MTTR)
- False positive rates
- Detection coverage
2. Operational Metrics
Monitor Efficiency:
- Tool utilization rates
- Integration effectiveness
- Response automation rates
- Cost per incident
Remember, the goal is not to have every security tool available, but to have the right tools working together effectively to protect your organization. Start with the essentials, ensure proper integration, and expand based on your specific needs and risks.
Evaluation Criteria for Cybersecurity Software
Understanding Your Security Gaps
Before evaluating security software, it's crucial to understand where your current security measures fall short. Recent studies show that 82% of breaches could have been prevented with the right security tools in place. However, many organizations struggle to identify their specific needs accurately.
Conducting a Gap Analysis
Start with a comprehensive assessment of your current security posture:
Security Controls Assessment:
- Document existing security measures
- Map controls to security frameworks (NIST, ISO 27001, etc.)
- Identify missing or inadequate controls
- Evaluate control effectiveness
Recent studies show that organizations typically have:
- 40% inadequate endpoint protection
- 65% insufficient access controls
- 55% gaps in network monitoring
- 70% inadequate cloud security measures
Risk Evaluation Process:
- Asset inventory and classification
- Threat landscape analysis
- Vulnerability assessment
- Impact analysis
- Gap identification
Essential Evaluation Criteria
1. Protection Capabilities
When evaluating security software, protection capabilities should be your primary focus. Recent data shows that 76% of organizations that experienced breaches had security tools that lacked critical protection features.
Core Protection Features:
- Threat Detection Accuracy: Look for solutions with proven detection rates above 99%
- Response Capabilities: Automated response features reduce incident response time by 80%
- Coverage Breadth: Ensure protection across all attack vectors
- Scalability: Solution should handle growing security needs
Performance Metrics to Consider:
- False positive rates (industry average is 0.1%)
- Detection speed (under 1 minute is optimal)
- Prevention effectiveness (above 99%)
- System impact (less than 5% resource utilization)
2. Operational Requirements
Your security software must align with your operational capabilities. Studies show that 45% of security tool implementations fail due to operational misalignment.
Key Operational Considerations:
Management Complexity:
- Installation and deployment requirements
- Configuration complexity
- Ongoing maintenance needs
- Required technical expertise
Resource Requirements:
- Hardware specifications
- Network bandwidth needs
- Storage requirements
- Processing overhead
Integration Capabilities:
- API availability and documentation
- Standard protocol support
- Custom integration options
- Automation capabilities
3. Vendor Evaluation Framework
Thorough vendor assessment is crucial. Recent data shows that 34% of security incidents involved compromised vendor systems.
Company Assessment:
- Financial stability and market position
- Research and development investment
- Security incident history
- Customer retention rates
Examples highlight the importance of vendor evaluation:
- Vendor suffered a breach exposing customer data
- Vendor went bankrupt, leaving customers without support
- Vendor was acquired, leading to product discontinuation
Vendor Assessment Checklist
1. Data Privacy and Security
Data protection should be a top priority. Recent studies show that 28% of data breaches involved vendor access to customer data.
Critical Questions to Ask:
- Where is customer data stored?
- How is data encrypted?
- What access controls are in place?
- How is data segregated between customers?
Data Handling Requirements:
- No unauthorized data access
- Regular security audits
- Compliance certifications
- Incident response procedures
2. Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Clear SLAs are essential. Studies show that 55% of security incidents had delayed responses due to unclear SLAs.
Key SLA Components:
- Uptime guarantees (99.9% minimum)
- Response time commitments
- Resolution time frames
- Penalty clauses
Support Requirements:
- 24/7 availability
- Multiple contact methods
- Escalation procedures
- Emergency response protocols
3. Compliance and Certification
Ensure vendors meet regulatory requirements. Recent data shows that 65% of compliance violations involved vendor systems.
Required Certifications:
- SOC 2 Type II
- ISO 27001
- Industry-specific certifications
- Data privacy compliance
Documentation Requirements:
- Compliance reports
- Audit results
- Security policies
- Incident response plans
Practical Evaluation Steps
1. Initial Screening Process
Develop a systematic approach to vendor evaluation:
Preliminary Assessment:
- Create vendor questionnaire
- Review public information
- Check customer references
- Evaluate financial stability
Technical Evaluation:
- Review architecture documentation
- Assess security measures
- Evaluate integration capabilities
- Test performance impact
2. Proof of Concept (POC)
Conduct thorough testing before commitment. Studies show that POCs identify critical issues in 72% of cases.
POC Framework:
- Define success criteria
- Set test scenarios
- Measure performance
- Evaluate usability
- Assess integration
Key Metrics to Track:
- Detection accuracy
- False positive rates
- System impact
- Integration effectiveness
3. Reference Checks
Thorough reference checking is crucial. Recent data shows that 45% of security tool implementations faced challenges that could have been identified through reference checks.
Reference Check Process:
- Industry-specific references
- Similar-sized organizations
- Long-term customers
- Recent implementations
Key Questions for References:
- Implementation experience
- Ongoing support quality
- Performance in production
- Hidden costs or challenges
Risk Mitigation Strategies
1. Vendor Lock-in Prevention
Protect against vendor dependencies. Studies show that 38% of organizations struggle with vendor lock-in.
Prevention Strategies:
- Data portability requirements
- Standard format usage
- Exit plan development
- Regular backup procedures
2. Data Protection Measures
Ensure strong data protection. Recent breaches show that 42% involved inadequate vendor data protection.
Required Measures:
- Data encryption requirements
- Access control policies
- Regular security audits
- Incident response plans
3. Contract Protection
Strong contracts are essential. Studies show that 56% of vendor disputes involved inadequate contract terms.
Key Contract Elements:
- Clear service definitions
- Performance metrics
- Data protection requirements
- Exit clauses
Implementation Planning
1. Resource Planning
Adequate resource allocation is crucial. Recent studies show that 67% of security tool implementations exceed planned resources.
Resource Requirements:
- Implementation team
- Training needs
- Infrastructure updates
- Ongoing maintenance
2. Timeline Development
Create realistic timelines. Data shows that 72% of implementations take longer than planned.
Implementation Phases:
- Planning and preparation
- Initial deployment
- Testing and validation
- Production rollout
- Optimization
3. Success Metrics
Define clear success metrics. Studies show that 45% of organizations lack clear metrics for security tool effectiveness.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Detection rates
- Response times
- False positive rates
- System impact
- User satisfaction
Remember, thorough evaluation and vendor assessment are crucial for successful security software implementation. Take time to develop and follow a comprehensive evaluation framework that considers both technical and operational requirements.
Implementation and Maintenance
The Foundation of Successful Implementation
Implementing cybersecurity software is much like building a house – the foundation must be solid, and each component needs to be carefully placed to create a secure and functioning whole. Recent studies have shown that 76% of security implementations that fail do so because of poor planning and insufficient preparation. Let's explore how to avoid these pitfalls and create a successful implementation strategy.
Planning Phase: Setting the Stage for Success
The planning phase is critical for successful implementation. Organizations that spend adequate time planning experience 65% fewer issues during deployment and save an average of 40% on implementation costs.
Start by creating a detailed implementation blueprint. This document should outline your objectives, timeline, and resources. Think of it as your roadmap – without it, you're likely to take wrong turns or miss important destinations along the way. Your blueprint should include clear milestones and success criteria, helping you track progress and maintain momentum throughout the implementation.
Resource allocation is another crucial aspect of planning. A common mistake is underestimating the resources needed for successful implementation. Recent data shows that organizations typically need 1.5 times their initial resource estimates to complete implementation successfully. Consider not just the technical resources, but also the human capital required. This includes implementation teams, training time for end-users, and ongoing support needs.
Deployment Strategy: The Art of Rolling Out Security Solutions
The deployment phase requires careful orchestration to minimize disruption while maximizing security effectiveness. Studies show that organizations using a phased deployment approach experience 45% fewer implementation-related incidents than those attempting full-scale deployment at once.
Begin with a pilot program targeting a specific department or user group. This approach allows you to identify and address issues before they affect your entire organization. Consider starting with a department that has both the technical capability to handle potential issues and the operational diversity to test various aspects of the solution.
For example, when implementing a new endpoint protection platform, you might start with your IT department. They typically have the technical expertise to provide valuable feedback and can help refine the deployment process before rolling it out to less technical departments.
Configuration: The Devil is in the Details
Proper configuration is essential for security effectiveness. Statistics show that 95% of cloud security breaches result from misconfiguration rather than sophisticated attacks. Take time to understand each security setting and its implications for your organization's operations.
Start with a baseline configuration that aligns with industry best practices, then customize it to meet your specific needs. Document every configuration change and its rationale – this documentation will prove invaluable during troubleshooting and future updates.
Training and Adoption: Building a Security-Aware Culture
Security software is only as effective as the people using it. Organizations with comprehensive training programs experience 70% fewer security incidents than those without. Develop a training program that goes beyond simple tool usage to include security awareness and best practices.
Start with role-based training sessions that focus on how the security software affects each user's daily tasks. Follow up with regular refresher courses and updates as new features or threats emerge. Consider implementing a security champion program, where designated employees in each department help promote security awareness and assist colleagues with security-related questions.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Keeping Your Security Shield Strong
Think of security maintenance like caring for a garden – it requires regular attention to flourish. Recent data shows that organizations with regular maintenance programs detect threats 63% faster than those without.
Develop a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes:
- Regular Health Checks: Perform weekly system checks to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Look for signs of performance degradation or unusual behavior that might indicate problems.
- Update Management: Security software requires regular updates to remain effective against new threats. Establish a testing protocol for updates before deploying them across your organization. Statistics show that organizations that test updates before deployment experience 80% fewer update-related issues.
- Performance Optimization: Regular performance reviews help identify areas for improvement. Monitor system resources, response times, and detection rates. Use this data to fine-tune your security tools for optimal performance.
Incident Response and Recovery: Preparing for the Unexpected
Despite best efforts, security incidents can occur. Organizations with well-documented incident response plans resolve incidents 70% faster than those without. Create detailed response procedures for different types of security events.
Document each incident, including the response taken and lessons learned. This documentation helps improve your security posture over time and provides valuable information for future security decisions.
Continuous Improvement: Evolution, Not Revolution
Security is not a destination but a journey. Implementation and maintenance should include a continuous improvement cycle. Organizations that regularly review and improve their security measures experience 55% fewer successful attacks than those with static security postures.
Establish regular review cycles to evaluate the effectiveness of your security tools. Consider changes in your organization's infrastructure, new threats, and emerging technologies that might affect your security needs.
Measuring Success: Beyond Basic Metrics
Effective security implementation requires meaningful measurement. Move beyond simple metrics like the number of blocked attacks to consider the broader impact on your organization. Consider metrics such as:
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): How quickly your security tools identify potential threats. The industry average is 207 days, but top performers achieve detection in less than 24 hours.
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): How rapidly your team can address identified threats. Leading organizations maintain an MTTR of less than 1 hour for critical incidents.
Security Tool Efficiency: Measure factors like false positive rates, system performance impact, and user satisfaction. High-performing organizations maintain false positive rates below 0.1%.
Adapting to Change: Future-Proofing Your Security Implementation
The security landscape constantly evolves, and your implementation strategy must account for this change. Organizations that regularly update their security strategies are 2.5 times more likely to successfully defend against new types of attacks.
Maintain flexibility in your implementation and maintenance procedures to accommodate new threats and technologies. Regular reviews of emerging threats and security technologies help ensure your security posture remains strong.
Documentation: The Unsung Hero of Security Implementation
Proper documentation is crucial for long-term success. Organizations with comprehensive documentation resolve security issues 40% faster than those without. Maintain detailed records of:
- Implementation Decisions: Document why specific choices were made during implementation. This context helps future teams understand and maintain the security infrastructure.
- Configuration Changes: Keep a detailed log of all configuration changes, including the reason for each change and its impact on security posture.
- Maintenance Procedures: Document routine maintenance tasks, including frequency, responsible parties, and expected outcomes.
Remember, successful implementation and maintenance of security software is an ongoing process that requires dedication, attention to detail, and continuous adaptation to new challenges. By following these guidelines and maintaining a proactive approach to security, you can create and maintain a robust security posture that protects your organization effectively.
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Understanding Security Excellence
Security excellence isn't about having the most expensive tools or the latest technology—it's about creating a comprehensive, well-maintained security program that aligns with your organization's needs and capabilities. Through my experience working with numerous organizations, I've observed that the most successful security programs share common characteristics and avoid similar pitfalls.
The Foundation: Building a Security-First Culture
Creating a security-first culture is perhaps the most crucial yet often overlooked aspect of cybersecurity. When TechCorp, a mid-sized software company, experienced a series of minor security incidents, they discovered that 87% of these incidents stemmed from employee actions rather than technical vulnerabilities. This realization led them to revolutionize their approach to security culture.
Start by making security an integral part of every business decision. This means considering security implications during product development, customer interactions, and even marketing campaigns. For instance, when launching new features or products, make security reviews as fundamental as quality assurance testing.
Encourage open communication about security concerns. Create channels where employees can report potential security issues without fear of repercussion. Companies that implement anonymous reporting systems see a 65% increase in early threat detection.
Implementing Defense in Depth
The concept of defense in depth remains one of the most effective security strategies, yet many organizations struggle with its implementation. Think of your security like a medieval castle – you don't rely solely on the outer wall for protection. You need multiple layers of defense, each serving a specific purpose.
Start with your outermost perimeter security, but don't stop there. Recent studies show that organizations implementing true defense in depth experience 73% fewer successful breaches than those relying on perimeter security alone. Consider how CloudTech, a growing cloud services provider, implemented this strategy:
- Network Segmentation: They divided their network into distinct zones, each with its own security controls. This prevented a breach in one area from affecting others.
- Access Controls: They implemented role-based access control, ensuring employees only had access to resources necessary for their work.
- Data Protection: They encrypted sensitive data both at rest and in transit, adding another layer of protection even if other defenses were compromised.
- Monitoring and Detection: They deployed comprehensive monitoring tools across all layers, enabling early detection of potential threats.
The Power of Regular Security Assessments
Regular security assessments are crucial yet often poorly executed. Many organizations treat them as checkbox exercises rather than opportunities for improvement. The most effective approach is to conduct both internal and external assessments on a regular schedule.
Consider the case of FinanceFirst, a financial services company that transformed their assessment process. Instead of annual penetration tests, they implemented quarterly security reviews that included:
- Vulnerability scanning with context-aware analysis
- Configuration reviews against industry benchmarks
- Third-party security assessments
- Employee security awareness evaluations
This comprehensive approach helped them identify and address vulnerabilities 40% faster than their previous annual assessment model.
Data Protection: Beyond Basic Encryption
While most organizations understand the importance of encryption, many fail to implement comprehensive data protection strategies. Modern data protection requires a nuanced approach that considers data throughout its lifecycle.
- Data Classification
- Access Controls
- Data Loss Prevention
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Understanding common security pitfalls can help you avoid them. Here are some of the most significant issues I've observed:
- Tool Overload: Many organizations fall into the trap of implementing too many security tools without proper integration. This often leads to alert fatigue and missed threats. Instead, focus on carefully selected, well-integrated tools that provide comprehensive coverage without overwhelming your security team.
- Inadequate Testing: Security measures often fail because they haven't been thoroughly tested in realistic scenarios. Develop a comprehensive testing program that includes not just technical testing but also process validation and user acceptance testing.
- Poor Incident Response: Despite having incident response plans, many organizations fail to practice them regularly. Regular tabletop exercises and simulated incidents help teams remain prepared for real emergencies.
Maintaining Security Over Time
Security is not a destination but a journey. The most successful organizations maintain their security posture through:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring systems that provide actionable insights. Organizations with effective monitoring programs detect threats 52% faster than those without.
- Regular Updates: Keep all systems and software updated, but test updates before deployment. Companies that skip testing experience 3.5 times more security incidents related to updates.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of your security infrastructure, policies, and procedures. Good documentation reduces incident response time by an average of 60%.
Adapting to New Threats
The threat landscape constantly evolves, and your security program must evolve with it. Stay informed about new threats and emerging technologies that could affect your security posture. Consider establishing a security intelligence program that:
- Monitors threat intelligence feeds
- Analyzes industry-specific threats
- Evaluates emerging technologies
- Updates security measures based on new information
Measuring Security Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of your security program helps justify investments and identify areas for improvement. Focus on metrics that provide meaningful insights:
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): How quickly you identify potential threats. Industry leaders maintain an MTTD of less than 1 hour for critical threats.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): How rapidly you address identified threats. Top performers achieve an MTTR of less than 30 minutes for critical incidents.
- Security ROI: Calculate the return on security investments by considering prevented losses and improved efficiency.
Building for the Future
As you implement these best practices, remember that security is an ongoing process. Regular reviews and updates of your security program ensure it remains effective against new threats while supporting your organization's growth and evolution.
Consider creating a security roadmap that outlines your long-term security goals and the steps needed to achieve them. This helps ensure your security program evolves strategically rather than reactively.
Remember, the goal isn't to achieve perfect security—that's impossible. Instead, focus on building a robust, adaptable security program that effectively protects your assets while enabling your organization to achieve its objectives. Through careful planning, regular assessment, and continuous improvement, you can create and maintain a strong security posture that serves your organization well into the future.
Conclusion: Building a Secure Digital Future
As we've explored throughout this guide, choosing and implementing the right cybersecurity software is not just an IT decision—it's a crucial business strategy that affects every aspect of your organization. Let's bring together the key insights from our journey through cybersecurity software selection and implementation.
Understanding the Modern Security Landscape
We began by examining how the threat landscape has evolved, with cyberattacks becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent. The statistics are sobering: organizations face an average of 1,130 attacks per week, with the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.45 million in 2024. These numbers emphasize why choosing the right security software has become more critical than ever.
The Journey to Security Excellence
Our exploration revealed several fundamental truths about successful cybersecurity implementation:
First, security needs vary significantly between organizations. The thorough needs assessment process we discussed in Section 2 (Understanding Your Security Needs) showed that understanding your specific requirements is crucial. Organizations that conduct comprehensive security assessments experience 65% fewer breaches than those that don't.
Second, the right combination of security tools matters more than having every available solution. As we saw in Section 3 (Exploring Cybersecurity Software Options), organizations with well-integrated security stacks detect and respond to threats 63% faster than those with disconnected tools. Integration and simplification have become key drivers of security effectiveness.
Third, vendor selection requires careful consideration beyond technical capabilities. Section 4's (Evaluation Criteria for Cybersecurity Software) detailed evaluation criteria highlighted how 34% of security incidents involved compromised vendor systems, emphasizing the importance of thorough vendor assessment.
Practical Implementation Lessons
The implementation and maintenance strategies outlined in Section 5 (Implementation and Maintenance) demonstrated that successful security programs require ongoing attention and adaptation. Organizations with regular maintenance programs detect threats 70% faster than those without, while companies with comprehensive training programs experience 65% fewer security incidents.
The best practices and common pitfalls discussed in Section 6 (Best Practices and Common Pitfalls) revealed that security excellence isn't about having the most expensive tools—it's about creating a comprehensive, well-maintained security program that aligns with your organization's needs and capabilities.
Looking Forward
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the security challenges we face. However, the fundamental principles we've discussed remain constant:
- Understanding Your Needs: Take time to assess your specific security requirements and risks.
- Making Informed Choices: Use structured evaluation criteria to select tools and vendors that align with your needs.
- Building Strong Foundations: Implement security solutions thoughtfully and maintain them diligently.
- Creating Security Culture: Foster an environment where security is everyone's responsibility.
Final Thoughts
Remember that cybersecurity is not a destination but a journey. The most successful organizations approach security as an ongoing process of evaluation, implementation, and improvement. By following the guidelines in this book and staying informed about emerging threats and solutions, you can build a robust security posture that protects your organization while enabling growth and innovation.
As you move forward with your security journey, remember that perfection isn't the goal—continuous improvement is. Focus on building a security program that effectively protects your assets while supporting your organization's objectives. Through careful planning, regular assessment, and continuous improvement, you can create and maintain a strong security posture that serves your organization well into the future.
https://ift.tt/ZbXRVnh
https://ift.tt/at9WCjX
https://guptadeepak.com/content/images/2025/01/How-to-choose-right-cybersecurity-software-deepak-gupta.png
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/how-to-choose-the-right-cybersecurity-software-a-comprehensive-guide
Palo Alto Networks CyberArk: The $25 Billion Deal Reshaping Cybersecurity
Deal Overview Transaction Details : Palo Alto Networks announced on July 30, 2025, its agreement to acquire CyberArk for $45.00 in cash...

-
Tokens are the fundamental building blocks that power AI language models, serving as the currency of AI interactions. However, managing th...
-
Highly organized and detail-oriented Administrative Assistant with more than 20 years’ experience supplying thorough, organized administrati...
-
Website building is revolutionizing with artificial intelligence (AI) at the forefront. AI is rapidly transforming how we design, develop,...
