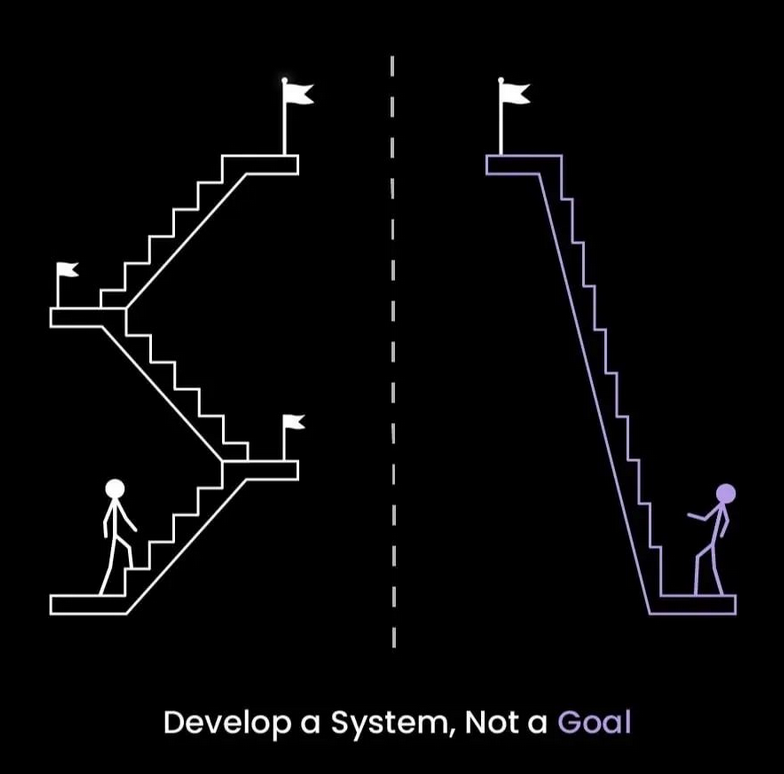
In the fast-paced world of tech entrepreneurship, goals are like stars – distant, luminous, and often seemingly unattainable.
A 2018 study found that while over 80% of tech startups set ambitious goals, only 25% consistently meet them. This gap between aspiration and achievement underlines a crucial insight: setting a goal is merely the first step. The crux of success lies in the systems and processes established to reach these objectives.
This article explores the necessity of robust systems for tech entrepreneurs, offering a blueprint for turning ambitious goals into tangible successes.
The Limitations of Goal-Setting Alone
Picture a journey to an uncharted destination without a map or compass.
This scenario mirrors the pursuit of a goal absent from a system. Goals offer direction but not a roadmap.
In the tech world, where innovation and adaptability are paramount, this lack of a systematic approach can lead to misdirection and inefficiency.
For instance, a tech startup aiming to revolutionize the AI industry with a new product might set a launch goal. However, this goal can quickly become unattainable and mired in operational chaos without a systematic approach—clear development stages, marketing strategies, and customer feedback loops.
The Power of Systems in Achieving Success
In entrepreneurship, a system is a coherent assembly of methods, habits, and strategies to achieve a goal. It’s the machinery that powers the journey to the destination.
For example, an entrepreneur’s goal might be to increase their app’s user base by 100% within a year. The system to achieve this could include specific marketing strategies, regular app updates based on user feedback, and partnerships with influencers. This systematic approach ensures every action is a step towards the goal, adaptable to feedback and market changes, making the process strategic rather than speculative.
Building an Effective System
Developing an effective system starts with deconstructing the goal into actionable steps and establishing short-term objectives.
For example, if an entrepreneur aims to launch a new software tool, their system could involve daily coding schedules, weekly brainstorming sessions, and bi-weekly user interface testing. This granular approach ensures steady progress towards the goal. Systems must evolve based on feedback and market dynamics. For instance, if user testing reveals a significant issue, the development schedule might be adjusted to prioritize this fix, reflecting the system’s adaptability.
Case Studies of Successful Systems in Tech
Consider Spotify’s journey. Their success is rooted in continuous innovation, agile development, and relentless user-focused enhancements. Their approach—encouraging team autonomy, frequent product iterations, and leveraging user data—enabled them to refine their service continuously and stay ahead in the competitive streaming industry.
Another example is Dropbox, which used a referral system as a growth strategy. This system incentivized current users to invite new users, significantly boosting its user base without traditional advertising.
Tips for Maintaining and Improving Your System
An effective system is dynamic, requiring regular evaluation and refinement. Implement periodic assessments to gauge system efficiency and adapt to new information or technologies.
For instance, a tech company might review its product development system quarterly, incorporating new software tools or methodologies to enhance efficiency. Cultivating a culture of feedback and continuous learning is vital. Encourage teams to embrace constructive criticism, experiment with new approaches, and learn from setbacks to foster a growth-oriented environment.
Learnings
Navigating the complexities of tech entrepreneurship demands more than goal-setting; it requires constructing and maintaining robust systems. These systems transform visionary objectives into achievable realities by providing a clear, adaptable pathway to success. Entrepreneurs can turn their starry ambitions into concrete achievements by focusing on systematic processes, embracing adaptability, and learning from each step.
The journey to success in tech is not just charted by the goals you set but, more importantly, by the systems that guide your path.
https://ift.tt/NhS8Brv
https://ift.tt/VDKouI9
https://guptadeepak.com/content/images/2023/11/build-a-system-not-a-goal.png
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/beyond-goals-developing-systems-for-success-in-tech




