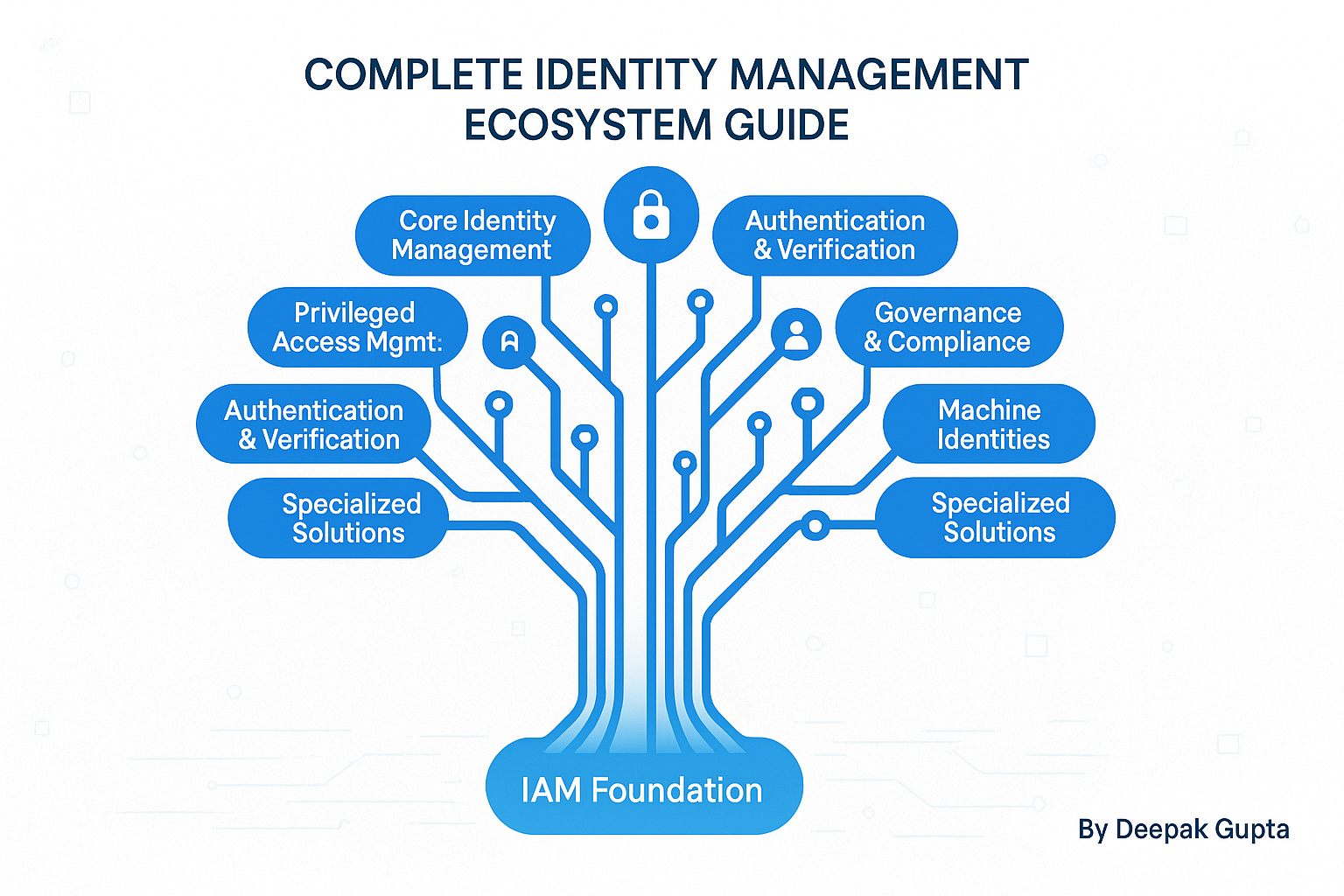
Deal Overview

Transaction Details: Palo Alto Networks announced on July 30, 2025, its agreement to acquire CyberArk for $45.00 in cash and 2.2005 shares of Palo Alto Networks common stock per CyberArk share, representing a 26% premium to CyberArk's 10-day average closing price. The total deal value is approximately $25 billion.
Timeline: The transaction is expected to close during the second half of Palo Alto Networks' fiscal 2026, subject to regulatory clearances and CyberArk shareholder approval.
Strategic Rationale: Why Palo Alto is Acquiring CyberArk
1. Platform Strategy Acceleration
Palo Alto Networks aims to establish Identity Security as a new core platform pillar, advancing the vision that "every identity, human, machine and AI requires deep security for access across the modern enterprise."
2. AI Agent Security Leadership
The acquisition positions the combined company to "deliver Identity Security for agentic AI to secure the new wave of autonomous AI agents by providing foundational controls for this emerging class of privileged identities."
3. Market Consolidation Play
CEO Nikesh Arora has been on an acquisition spree since 2018, building a comprehensive cybersecurity platform. This year alone, Palo Alto bought Protect AI and has acquired multiple companies including Talon Cyber Security, Dig Security, and Zycada Networks in 2023.
4. Addressing Identity Gap
Palo Alto Networks - "long a dominant force in network and cloud security, has been aggressively expanding its footprint into AI and security operations" but lacked a strong identity security foundation that CyberArk provides.
What They're Planning to Do
Immediate Integration Goals
According to Palo Alto CEO Nikesh Arora's shareholder letter, the combined company will "optimize our combined go-to-market resources and continue to lead innovation" with the goal to "double the value of our joint businesses over the next five years."
Product Strategy
By combining "Palo Alto's platform scale with CyberArk's specialized expertise," the deal creates "a unified platform that spans network security, AI protection, and identity-driven threat mitigation."
Market Expansion
CyberArk will leverage Palo Alto's scale to:
- Deepen their penetration in PAM
- Target the significantly larger base of global IAM users and machine identities
How This Will Shape the Cybersecurity and Identity Industry
1. Industry Consolidation Acceleration
The deal aligns with broader consolidation trends: In 2024 alone, the cybersecurity sector saw a 30% increase in M&A activity, driven by the need to address fragmented security stacks and AI-driven threats.
This represents "one of the largest cybersecurity deals thus far in 2025," following Google's $32 billion acquisition of Wiz in March.
2. Platform vs. Point Solution Shift
The acquisition reflects the market's move away from fragmented solutions: The Identity Security category is highly fragmented with over one hundred vendors vying to capture the customer's attention across multiple functional domains. These domains are converging as the complexity of stitching together disparate solutions and the rise in identity-related breaches push enterprises to favor better integration."
3. Competitive Landscape Reshaping
The combined entity will directly challenge Okta and Ping Identity in the identity and AI security spaces, while potentially eliminating standalone IAM players like SailPoint and One Identity, which lack the integration and AI capabilities of a combined PANW-CYBR platform.
4. AI Agent Identity Management Leadership
The timing is strategic as 81% of security leaders now consider machine identity security vital for safeguarding AI systems, and 72% plan to prioritize protecting AI models from compromise.
Impact on the Identity Ecosystem
The writing was on the wall: When I started in identity management 12 years ago, I had clear categories. CIAM for customers, traditional IAM for employees, PAM for privileged access. Clean boundaries, distinct markets. That world is gone.
Market Dynamics
- PAM Market: CyberArk's dominance with over 55% of the Fortune 500 and over 8 million privileged end users now comes under Palo Alto's platform umbrella, creating the first major network-to-identity integrated platform
- CIAM Landscape Already Consolidated: The customer identity space has already undergone significant consolidation with Okta acquiring Auth0 (2021, $6.5B) and Thoma Bravo merging Ping Identity and ForgeRock. This leaves a concentrated field of Okta-Auth0, the Ping-ForgeRock combination, Microsoft Entra ID, AWS Cognito, and cloud-native players. Palo Alto's move signals that network security vendors may now target the remaining independent identity players.
- Machine Identity: The combined company will lead in securing AI agents and machine identities, a rapidly growing segment where traditional CIAM players have limited presence
The Platform Play is Everything
This isn't just about Palo Alto buying CyberArk—it's about the fundamental shift from best-of-breed to platform-first thinking. As someone who built a successful standalone CIAM solution, I understand both the power and limitations of specialized tools.
The reality today: CISOs are tired of managing 50+ security tools. They want platforms that provide integrated experiences, shared threat intelligence, and unified policies. Palo Alto just bought their way into that integrated future.
Broader Consolidation Implications
This deal accelerates a trend where platform vendors (Palo Alto, Microsoft, Google) are absorbing specialized identity providers rather than competing identity vendors merging with each other. We're seeing:
- Horizontal consolidation (identity + identity) already completed in CIAM
- Vertical integration (network security + identity) now beginning with Palo Alto-CyberArk
- Cloud giants (Microsoft, Google, AWS) strengthening their identity offerings organically
The remaining independent identity players—whether specialized (like workforce IAM vendors) or regional CIAM providers—now face pressure from both consolidated identity competitors AND platform vendors expanding into identity.
Technology Integration - Network, Cloud and Identity
CyberArk's expertise in certificate lifecycle management, zero-standing privilege (ZSP) strategies, and adaptive access governance aligns perfectly with Palo Alto's vision of a holistic, risk-aware security architecture.
This creates the first truly integrated security platform spanning network, cloud, and identity—something the previously consolidated identity-only players cannot match without their own platform acquisitions.
Industry Trends This Deal Validates
1. Identity as the New Perimeter
Identity will remain both a cornerstone of security and one of its biggest vulnerabilities going forward.
2. AI-Driven Identity Management
The industry is moving toward "agentic AI" systems that provide "autonomous, context-aware decision-making systems" for identity management.
3. Machine Identity: The New Battleground
Organizations now manage "a 40:1 ratio of machine identities to human ones," with "50% of organizations expecting identity management loads to triple soon due to non-human machine identities."
Traditional IAM providers missed this boat. While Okta and others focused on human customer identity, the real growth was happening in machine-to-machine authentication, service accounts, and now AI agent identities. CyberArk understood this early with their machine identity focus—that's what makes this acquisition so strategic.
Market Reaction and Implications
Market response was mixed: "CyberArk shares soared 13% on Tuesday after The Wall Street Journal reported" the potential deal, while "Palo Alto shares, meanwhile, slid 5% on the report."
The Innovation Dilemma
Here's what concerns me as an entrepreneur: Platform consolidation often kills innovation. When you're managing a $25 billion integration, your focus shifts from breakthrough innovation to seamless integration.
The opportunity gap: This creates space for nimble startups to solve emerging problems—like AI agent identity management, zero-trust CIAM, or privacy-preserving authentication—while the giants focus on integration.
Implications for Different Players
For Remaining Independent Identity Vendors
If you're running an independent identity company right now, you have three options:
- Get acquired fast by Microsoft, Google, or another platform vendor
- Go ultra-specialized in areas the platforms won't touch (like privacy-focused identity)
- Build your own platform (extremely capital-intensive)
The middle ground is disappearing. You can't compete on features alone when customers want integrated platforms.
For Startups in the Identity Space
This is actually good news for innovation. Large platform integrations create gaps:
- AI agent identity management (still nascent)
- Privacy-preserving identity solutions
- Industry-specific identity needs
- Next-generation authentication methods
My advice: Don't try to build another general-purpose IAM platform. Find the specific identity problems that platforms can't solve well and own those niches.
For Enterprise Buyers
Short-term pain, long-term gain. You'll see integration challenges, feature conflicts, and probably some price increases as Palo Alto optimizes the combined offering.
But the strategic value is real: Having network security, cloud protection, and identity management in one platform with shared threat intelligence and unified policies? That's worth the integration headaches.
The AI Agent Identity Challenge
AI agents aren't just fancy service accounts—they make autonomous decisions, access multiple systems, and operate with varying levels of privilege based on context.
CyberArk's PAM foundation gives Palo Alto a head start here, but the real innovation is still ahead of us. We need identity solutions that can:
- Grant AI agents contextual privileges based on their current task
- Revoke access when AI behavior becomes anomalous
- Audit AI decision-making for compliance
- Scale to millions of AI agents per organization
This is where the next wave of identity innovation will happen.
The Bigger Picture: From Product-Led to Platform-Led
The market has spoken: customers want platforms, not products.
What this means strategically:
- Customer acquisition will increasingly happen at the platform level
- Individual identity features become table stakes
- Innovation happens through platform integration, not standalone capabilities
- Pricing power shifts to platform vendors
My Prediction: What Happens Next
- Microsoft will make a major identity acquisition within 18 months (probably targeting workforce IAM)
- Google will build, not buy (they prefer organic platform development)
- AWS will acquire a specialized player (maybe in the machine identity space)
- CrowdStrike will need an identity play to compete with the new Palo Alto platform
The innovation opportunity: While the giants consolidate, startups that solve emerging identity challenges—especially around AI, privacy, and industry-specific needs—will have 2-3 years to establish strong positions before the next consolidation wave.
Bottom Line
This deal represents the maturation of the identity market. The days of pure-play identity vendors competing primarily on features are ending. The future belongs to integrated security platforms with identity as a core pillar.
For entrepreneurs: Focus on the identity problems that platforms can't solve elegantly.
For enterprises: Embrace platform consolidation, but plan for integration complexity.
For the industry: This accelerates innovation in AI agent identity—the next big frontier.
As someone who's built identity solutions and now works in AI-powered scalable platform, I see this as validation of where the market was heading. The question isn't whether platform consolidation will continue—it's which specialized identity problems will emerge as the giants focus on integration.
That's where the next wave of identity innovation will happen.
https://bit.ly/41ml7Su
https://bit.ly/40NRyJA
https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1563688139-bb5832571d4b?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=max&fm=jpg&ixid=M3wxMTc3M3wwfDF8c2VhcmNofDI0fHxkZWFsJTIwZnV0dXJlfGVufDB8fHx8MTc1NDAyODI2OXww&ixlib=rb-4.1.0&q=80&w=2000
https://guptadeepak.weebly.com/deepak-gupta/palo-alto-networks-cyberark-the-25-billion-deal-reshaping-cybersecurity